Unexpected Cloud Challenges that CIOs Encounter
Cloud technology has transformed the way businesses run and so far companies that have adopted cloud have gained scalability, flexibility, optimum use of IT resources, reduced operational cost, and much more. However, cloud technology also presents some unique challenges. If not managed properly, these challenges can lead to chaos and thus be costly to your company. As a Managed Cloud Services provider, ExterNetworks has outlined a few of these complex challenges based on cloud technology’s functionality.
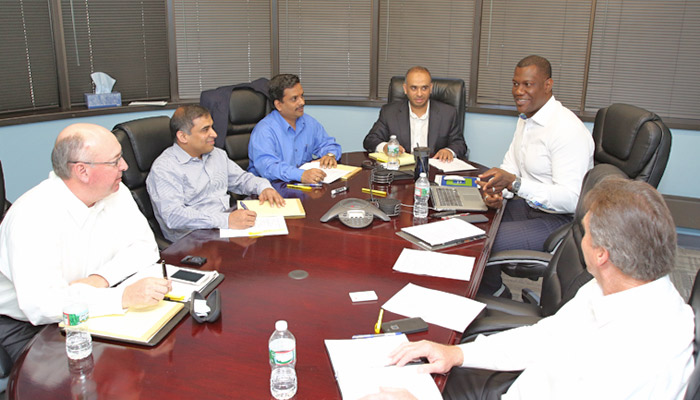

ExterNetworks’ Thought Leaders (from left): Allan stuke (Vice President of BD), Abdul Moiz (Senior Director), Harry Bodd (COO), Malik Zakaria (CEO), Les Williams (CMO), and Gary McCauley (Director of National Accounts) – addressing the evolving cloud challenges.
Migrating Everything to the Cloud
To stay competitive in the market, thought leaders must take the initiative to adapt to changing business trends and switch to cloud technology. This switch means migrating of all your company’s sensitive data and infrastructure off premise. Problems arise during migration when poor transitioning with vulnerable authentication processes results in data leakage, which not only impacts a company’s reputation but also compromises its clients’ proprietary information.
Traditional Applications Compatibility
Some of the traditional infrastructure and applications are not transferable or not as likely to be compatible with the cloud platform, so these applications have to be rewritten to support a modern framework.
Bandwidth and Cost of Migration
According to Cloud adoption surveys, some of the significant benefits of Cloud are its feasibility and accessibility of stored data. However, if the Cloud is not managed efficiently, the network and WAN bandwidth flexibility can become complicated. Cloud vendors offer adequate internal cloud bandwidth and flexibility to migrate files and applications, however if your network isn’t up and has a latency bottleneck, then it can negatively impact the transition. Therefore, before deploying your software and migrating data, it is vital to understand your migration requirements for efficient planning of network capacity and adequate optimization strategies to deal with possible network congestion
Post Cloud Migration Hurdles
In the Public cloud or a multi-tenancy environment, an inadvertent mistake into the database by one of the tenants can allow hackers to infiltrate the system and steal the data. The other hurdle in post migration is when a bug in the SSL protocol gives hackers the ability to intercept the encrypted data transmission and decrypt the process to intrude into the Cloud’s database. A cloud outage can temporarily halt your business operations.
ExterNetworks’ CEO, Malik Zakaria says,
“To ensure business continuity, it is necessary to maintain your cloud configuration by proactively monitoring the network, balancing cloud workload and performance, ensuring that security performance is at an optimum level, and automating the cloud storage backup.”
To accomplish this, you will need a team of skilled network managers and cloud engineers with hands-on experience. These skills however, don’t come cheap. With budget constraints and a fluctuating economy, it is costly to hire IT staff to proactively monitor cloud performance 24×7 while resolving other technical issues.
Advancing Cyber Attacks Are Challenging Cutting Edge Cloud
Cybercrime is on par with emerging technologies thus making cloud security one of the major security concerns facing many companies and organizations. Cyber criminals have successfully breached networks that use Cloud applications.
Cloud provides flexibility by authenticating users to access and circulate cloud-hosted data across the web. With a Single Sign-On (SSO) security feature, users can access all the applications and files in one go, instead of managing a large number of passwords. Apart from this great benefit, SSO also poses a massive vulnerability. If hackers breach the SSO, they can gain access to all the accounts under that authentication.
The BYOD feasibility that Cloud offers poses a persistent challenge to cloud’s security as many of these devices are hidden on the other side of the enterprise firewall or in a less secure environment. BYOD is more likely to allow hackers to intrude into the network through vulnerable applications. In multi-tenant cloud services or a public cloud platform, where you host user data, a substantial threat to attack revolves around user negligence, which can allow hackers to breach the system and steal critical data.
Altogether, data encryption, monitoring unusual behavior, and threat management through a preliminary approach can defend against any potential cyber attack.
Lack of Cloud Technology Skills
Experts in the field must handle technology enablement. As a result of the rise in cloud adoption and technology evolution, there is a shortage of cloud skills in the market. This shortage can create shadowy pitfalls for a company if it allows Cloud engineers who lack the knowledge to deploy and manage cloud virtualization architecture to do so. Organizations need to hire IT staff with the following cloud skills: Software Architect, Security Specialist, Data Center Manager, Business Liaison to mitigate cloud operations risk, and so on.
Lack of Support from Small Providers
It is likely that you may face issues such as failure of critical applications or systems post-migration, and you may not get prompt and immediate customer support. These are costly scenarios. In this situation, any delay in responding to resolve critical issues can land your business in trouble.
Bandwidth Cost – Emergence of IoT
Beyond security, other issues such as bandwidth and latency are critical too. Data-rich applications need high bandwidth network to avoid latency and timeout failures. Inappropriate network bandwidth optimization impacts cloud’s performance. As IoT and Cloud converge, zeta bytes of data are generated from diverse traffic sources. “In the wake of IoT adoption and the increased contention for bandwidth right-sizing becomes a critical factor for capacity planning of the Cloud,” says Les Williams, ExterNetworks’ CMO. He further states, “Before migrating to the cloud, IT managers must evaluate and test applications to permanently avoid bottlenecks and optimize their network through WAN optimization controllers.”
Embracing The Right Cloud Type
With plenty of cloud offerings in the market today, choosing the cloud solution that fits your needs can be somewhat confusing. You can rely on the expertise of technology partners or managed cloud services providers who can provide a tailor-made solution to meet your business needs. A strategic cloud model will help you to leverage your business operations and minimize technology cost.
Shadow IT Cloud Computing
With the extensive use of the cloud to drive profits, staying competitive and augmenting employee collaboration, organizations are relying on the latest technology. The use of third-party software or hardware that doesn’t comply with a company’s IT policy will lead to Shadow IT. This situation can pose an enormous security threat that may expose your enterprise’s critical data to cyber attack. For example, if a negligent employee stores sensitive data on Dropbox, apart from intellectual property loss, it might also impact the bandwidth of your network.
Mobile Device Management
Consumerization of IT has made adoption of enterprise mobility less complicated. However mismanagement of these mobile devices might open up your network to attacks. According to IDG survey, 74% of companies have gone through security breaches because of vulnerable mobile security. The University of Cambridge finds 87% of Android apps are vulnerable to cyber attacks. Mobile devices with unsafe applications introduce doorways for cyber criminals to intrude on an enterprise’s network through malware or spyware and capture user data. Strategic BYOD policies can mitigate some of the mobile security concerns for the cloud.
Cohesively Manage Cloud Providers
Running critical data on multiple cloud providers mitigates the loss of data. During a server outage or other failures, you can use one of the redundant clouds for business continuity. However, to manage multiple providers, you must plan to manage accounts, billing, administrations controls, sync, and others, to maintain consistency across multiple service providers.
Switching Cloud Providers
Cloud pricing varies from vendor to vendor. Initially, a few cloud providers might offer services at competitive prices and later increase the pricing for critical services. Small Cloud service providers are more likely to experience frequent outages, or at worst, they can shut down their business entirely. Enterprises can also experience bad customer service from a vendor. These scenarios can make a disgruntled customer move their business to other flexible cloud providers. However, switching to a different cloud provider can be challenging. For example, when you choose a vendor and customize the cloud API as per your application and data requirements, your application combines with their services leading to a vendor-lock-in situation and making the transition incompatible to a new vendor’s services.
The other challenge of shifting providers is when you migrate years of archived data – migration uses more bandwidth- which will incur additional costs and increase the chances of data loss. Additionally, the data has to be pulled back to on-premises storage and transformed into a traditional format to support the new vendor’s Cloud APIs.
Conclusion:
Managing bandwidth and security, hiring advanced cloud engineers, coordinating between different cloud providers – all of this needs substantial IT resources. You can turn to a trusted Managed Cloud Services Provider to handle the exhausting responsibility of managing your cloud while you focus on your business strategies.